Prerequisites¶
For this use case we will assume FD.io VPP is installed. We will also assume the user can create and start basic virtual machines. This use case will use the linux virsh commands. For more information on virsh refer to virsh man page.
The image that we use is based on an Ubuntu cloud image downloaded from: Ubuntu Cloud Images.
All FD.io VPP commands are being run from a su shell.
Topology¶
In this case we will use 2 systems. One system we will be running standard linux, the other will be running FD.io VPP.
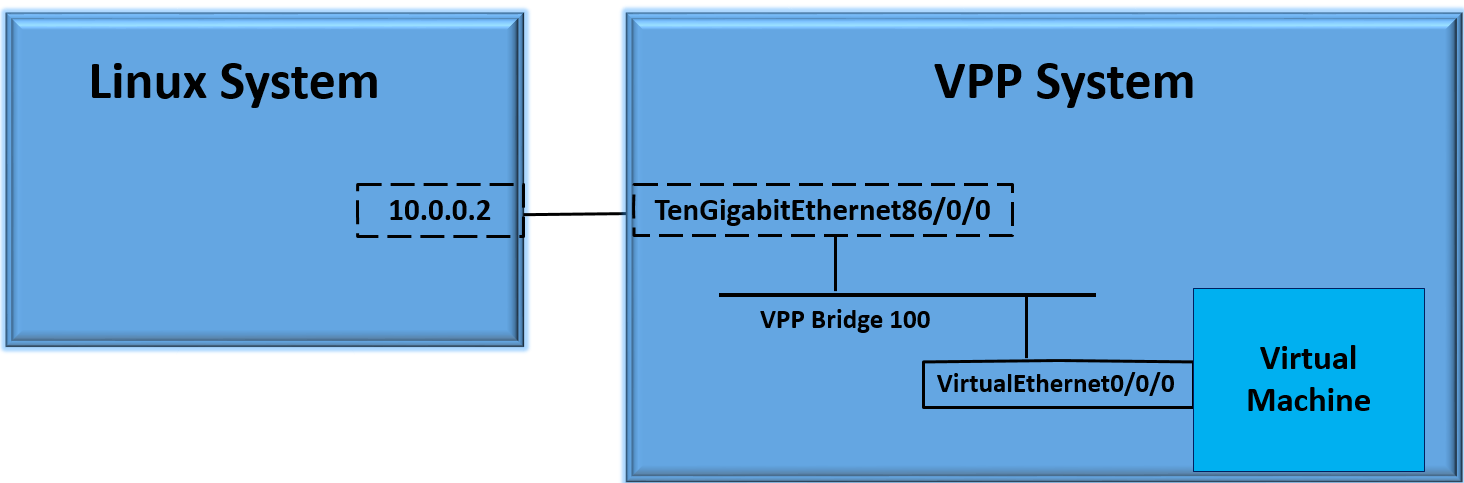
Vhost Use Case Topology¶
Creating The Virtual Interface¶
We will start on the system running FD.io VPP and show that no Virtual interfaces have been created. We do this using the Show Interface command.
Notice we do not have any virtual interfaces. We do have an interface (TenGigabitEthernet86/0/0) that is up. This interface is connected to a system running, in our example standard linux. We will use this system to verify our connectivity to our VM with ping.
$ sudo bash
# vppctl
_______ _ _ _____ ___
__/ __/ _ \ (_)__ | | / / _ \/ _ \
_/ _// // / / / _ \ | |/ / ___/ ___/
/_/ /____(_)_/\___/ |___/_/ /_/
vpp# clear interfaces
vpp# show int
Name Idx State Counter Count
TenGigabitEthernet86/0/0 1 up
TenGigabitEthernet86/0/1 2 down
local0 0 down
vpp#
For more information on the interface commands refer to: Interface Commands
The next step will be to create the virtual port using the Create Vhost-User command. This command will create the virtual port in VPP and create a linux socket that the VM will use to connect to VPP.
The port can be created using VPP as the socket server or client.
Creating the VPP port:
vpp# create vhost socket /tmp/vm00.sock
VirtualEthernet0/0/0
vpp# show int
Name Idx State Counter Count
TenGigabitEthernet86/0/0 1 up
TenGigabitEthernet86/0/1 2 down
VirtualEthernet0/0/0 3 down
local0 0 down
vpp#
Notice the interface VirtualEthernet0/0/0. In this example we created the virtual interface as a client.
We can get more detail on the vhost connection with the Show Vhost-User command.
vpp# show vhost
Virtio vhost-user interfaces
Global:
coalesce frames 32 time 1e-3
number of rx virtqueues in interrupt mode: 0
Interface: VirtualEthernet0/0/0 (ifindex 3)
virtio_net_hdr_sz 12
features mask (0xffffffffffffffff):
features (0x58208000):
VIRTIO_NET_F_MRG_RXBUF (15)
VIRTIO_NET_F_GUEST_ANNOUNCE (21)
VIRTIO_F_ANY_LAYOUT (27)
VIRTIO_F_INDIRECT_DESC (28)
VHOST_USER_F_PROTOCOL_FEATURES (30)
protocol features (0x3)
VHOST_USER_PROTOCOL_F_MQ (0)
VHOST_USER_PROTOCOL_F_LOG_SHMFD (1)
socket filename /tmp/vm00.sock type client errno "No such file or directory"
rx placement:
tx placement: spin-lock
thread 0 on vring 0
thread 1 on vring 0
Memory regions (total 0)
Notice No such file or directory and Memory regions (total 0). This is because the VM has not been created yet.